Biometry
Optical Biometry, also known as A-Scan, utilizes ultrasonic waves to measure eyeball length. Measuring the eyeball length is very important to manage a myopic patient. In any myopia clinic, these values would help to determine the ideal myopia control strategy.
It is also used to calculate the power of the Intraocular Lens to be implanted in the eye post-cataract surgery. The technician will instill anesthetic eye drops to numb the eye. Readings are taking with a probe brought to the eye. In the new generation instruments known as optical bio meters, the accuracy is better as readings are taken without patient contact. Both procedures are safe, and results are provided immediately.
Colour Vision Test:
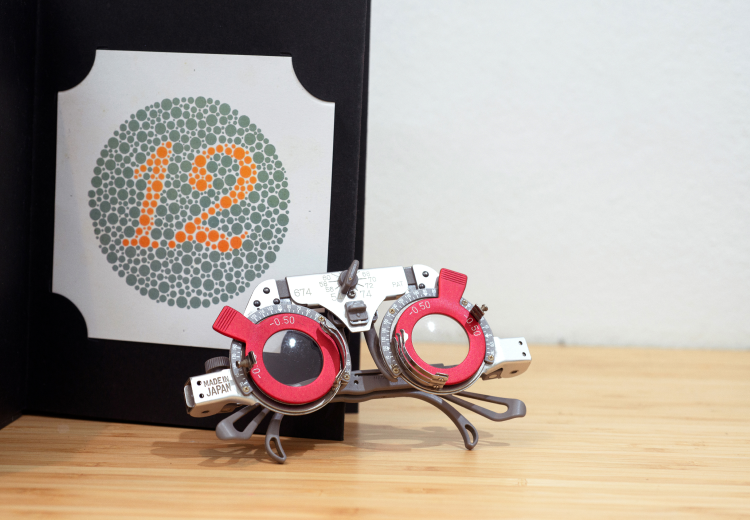
A Colour vision test is used to assess the ability of eyes to distinguish colours. Usually, a book with different plates called the Ishihara Color vision test is shown to you and asked if there is any number written on the template or not. You have to read the number on the plate or recognize the pattern. This test is performed for each eye. Loss of ability to differentiate colour may be by birth or acquired due to a disease or the side effect of medicine few medicines. There are other tests than Ishihara plates to check colour vision.
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography (FFA)
FFA is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate blood flow in blood vessels at the back part of the eyes. A special instrument photographs the blood flow patterns and captures any leakage after injecting a dye into the blood.
If the eye doctor has requested for FFA, the prerequisites for the test should be understood well. Fasting would be required prior to examination. Drops would be instilled in the eyes to dilate pupils for a better view.
Contact lens wearers should wear glasses and avoid lenses. Because of the dilated pupil, the vision would be blurry esp. for near, till the eye drop effect wears off. It is better to have an attendant to drive home.
The process usually takes up to 20-25mins. Usually, there are no side effects of the dye unless you are allergic to the dye itself. If dizziness, nausea, vomiting occur post-test, inform the doctor immediately.
Your skin and urine colour might be yellow for up to 24-48 hours. Plenty of water will help flush the dye out of the system. This test helps eye care practitioner to diagnose the disorders and plan the treatments for conditions that affect the blood vessels of the back part of the eyes.
Fundus Imaging:
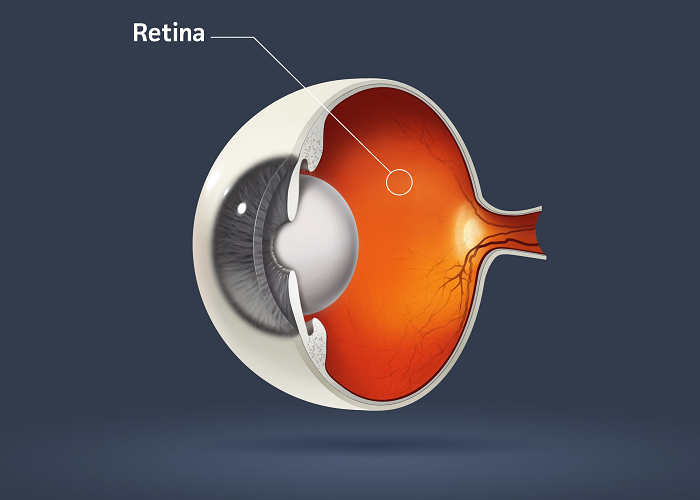
Fundus, the back part of the eye, also known as the retina, is an essential part of our visual system. It can be compared with the film of olden generation cameras. Any abnormality here should be detected as early and possible. Most of the ailments can be treated / delayed if diagnosed early. Once the disease sets in, we may not be able to recover the vision back in few cases.
For recording purpose and also to diagnose the condition, the eye doctor may take photographs of the retina with a fundus camera. Dilating the eyes will help the doctor to cover a larger area of your retina to photograph.
It is better to have an attendant drive back home and avoid wearing contact lenses for this test.
Optical Coherence Tomography:
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive, painless diagnostic procedure that helps the eye care practitioner to capture images and 3D cross-sections of various areas in the eye. These images can help the eye doctor to diagnose many conditions at an early stage.
Many eye diseases can go undetected until they reach a fairly advanced stage. OCT can pick these at a very early stage. This procedure is done in a sitting position and needs about a minute to be completed.
Ophthalmoscopy:
Ophthalmoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that allows your eye care practitioner to evaluate the retina. The retina is a very important part of the eye, relays visual information to the brain. Any abnormality in the retina can affect your eyesight.
Ophthalmoscopy can be direct where the eye doctor will have a handheld instrument that helps him see the insides of an eye. In indirect ophthalmoscopy, you will be asked to lie down on an examination chair keep your face towards the roof. Using the microscope and handheld magnifying lens, he assesses the retina.
Both techniques are non-contact techniques and are very safe. Exposure to light may make the vision blurry for few minutes till the eyes recover. The findings may be documented.
Going with an attendant is preferable and avoid wearing contact lenses for this test.
Photography:
Photography is an important part of the documentation. If there is any eye-related disorder, your eye doctor may take a photograph of it with special instruments to record it. By this, they can record the increasing severity of any disease that may affect the eyeball's standard structure. The eye doctor may use a camera attached to a slit lamp or use a DSLR camera to capture the images and file them.
Slit-lamp Examination:
Slit-lamp bio-microscope is an instrument with a low powered microscope and high-intensity light, which gives an excellent view of different parts of the eye. Also, various attachments can be used with this instrument to see otherwise challenging to reach areas.

It can get virtual cross-sections of the eyes transparent parts like the cornea and the lens. Eyelids, lashes, conjunctiva, cornea, sclera, anterior chamber, crystalline lens, vitreous chamber, retina all areas can be examined in great detail. This process can take up to several minutes.
This instrument is also necessary to examine all types of contact lens fittings to ensure that lens wear is safe for the eyes.
Spectacle Markings:
Irrespective of the age and type of spectacle you're wearing, it is essential that the fame and lenses fitted are according to eye and face measurements other than being according to the prescription.
Pre-fit markings on the frame like centration, height, facial wrap, pantoscopic tilt and many more need to be assessed based on power, requirement and lens design. The marking of progressive addition lenses or multifocal lenses that allow seeing distance intermediate and near special devices is attached to the frame for markings. This helps to design progressive lenses with better precision.
Spectacle marking is also crucial for single vision lenses with high powers. If the lens center is aligned with the eye center, the patient will experience a smooth, crisp and sharp vision without distortions. On few occasions, de-centration may be required.
Tear Function Tests:
Quantity assessment
Tear function test is an essential diagnostic procedure that evaluates the production, flow and drainage of tears.
A test called Schirmer's test is performed to check the tear production. The ECP will put a special kind of strip in the lower lid of the eyes and request to sit with eyes closed. After 5 minutes length of the strip wet with tears is measured. Lower values indicate that tear production is less and vice versa.
Good tear production is essential to keep eyes moist and healthy. After flowing across the eye, the tears get drained into the nose.
Quantity assessment
The tear film needs to stay spread over the eyes for 10 seconds or more. This is required to smooth out any microscopic irregularities, thus providing a clear vision and also to provide a protective layer to the eyes.
Tears are made of 3 layers – Closest to the eyes is the mucous layer that helps the tear film stick to the eyes. The second is the watery layer that provides comfort and wetness. The last layer exposed to the atmosphere is the oily layer or the lipid layer. This is the test for assessing the oily payer. A dye is instilled in the eye that stains the tears. The time taken for the lipid protective layer to break is noted. A reading over 10 seconds is normal.
When the oily layer's quality is affected, the tears evaporate faster, causing a dry feeling. The blinking also increases in frequency, and discomfort sets in.
Drainage assessment
The Jones dye test can check drainage. A dye is instilled in eyes that would drain out inside the nose. A sterile cotton bud is held inside the nostrils to check for dye drainage. This procedure is usually painless and harmless.
If your ECP suspects any problem in drainage, another test where a saline solution is injected with a syringe and special bent cannula in the puncta, which is an opening at the nasal corner of your eyelids. Saline solution draining out at the other end without any obstruction indicates normal findings. If saline solution gets obstructed, further investigations may be required.
Tonometry:
Tonometry is a diagnostic procedure in which intraocular pressure (IOP) of the eyeball is measured with basic to advanced instruments. The eye's normal pressure is around 12-16mmHg (millimeter of mercury).
A high or low pressure indicates glaucoma. This test is performed using the applanation tonometer attached to the slit lamp after instilling local anesthetic and a coloured dye in the eyes.
An air puff is blown on to the eye, and pressure required to change the curvature of the eye is measured. Other portable intraocular pressure measuring devices may be used.
This test plays a vital role in diagnosing sight-threatening conditions like glaucoma. If there is suspicion of glaucoma, more tests may be recommended for its confirmation.
Visual Field Testing:
Visual Field can be defined as seeing area (or field), which indicates the correct functioning of the back part of the eye. Visual Field test is used to determine central and peripheral vision. This test is recommended if glaucoma is suspected. It will help the eye doctor understand how much of the back part of the eye is damaged.
Refractive Error: -
In the normal (Emmetropic) Eye, when light rays enter, they focus on the retina, forming the sharp image that is further transmitted to the brain. Refractive error occurs when the eyes cannot focus light on to the retina, which can cause blurry vision. Simple eye examination can diagnose this. There are several types of Refractive error – Myopia, Hypermetropia and Astigmatism.
- Myopia (nearsightedness) – In this type of refractive error, the rays focused in front of the retina because either the cornea is too steep or the length of the eyeball is more than the normal Value. Distant vision is blurred, but the objects at near can be seen clearly in this type of Refractive error. This Can be corrected with Minus Lenses and Contact Lenses.
- Hypermetropia (farsightedness) - In this type of refractive error, the rays focused behind the retina because either the cornea is flat or the Length of the Eyeball is shorter than Normal Value. Children can see clearly for distance and near because they have the required accommodation whereas adults cannot see for distance and near. This can be corrected with Plus Lenses and contact lenses.
- Astigmatism - In this type of Refractive error, the light does not focus evenly on the retina. The patient sees the Distorted Vision at all distances. Glasses and Contact lenses are used, but they have to be toric to correct the Astigmatism.
- Presbyopia – It is the condition that generally occurs after the age of 40. Here the patient Gradually loses their ability to focus clearly for near, because of the age-related changes that start to occur in the Crystalline Lens. This can be corrected by using the glasses for near.
Corneal Conditions –
The cornea is the transparent outer part covering the black/brown region (Iris) of the eye. This layer helps the light to focus on the retina and helps in getting clear vision. There are several Corneal Conditions that can affect vision eventually –
- Scar/ Injuries- Small scratches (abrasions) on the cornea, those occur because of external injury. Superficial injuries heal on their own, and deeper can cause scarring and vision-related issues.
- Keratitis- is an inflammatory condition of the cornea in which redness and swelling can be seen. This can cause because of microbial Infection, allergy.
- Allergies – This can occur if there is an allergy to dust, pollens that can irritate the eyes. Itching is an indicative sign.
- Corneal Dystrophies – These are cornea disorders, which change its normal shape, and curvature. They can be inherited from one generation to other. Corneal Dystrophies are progressive in nature and, once they get worse, can cause pain and affect vision severely if not diagnosed and managed at the right time.